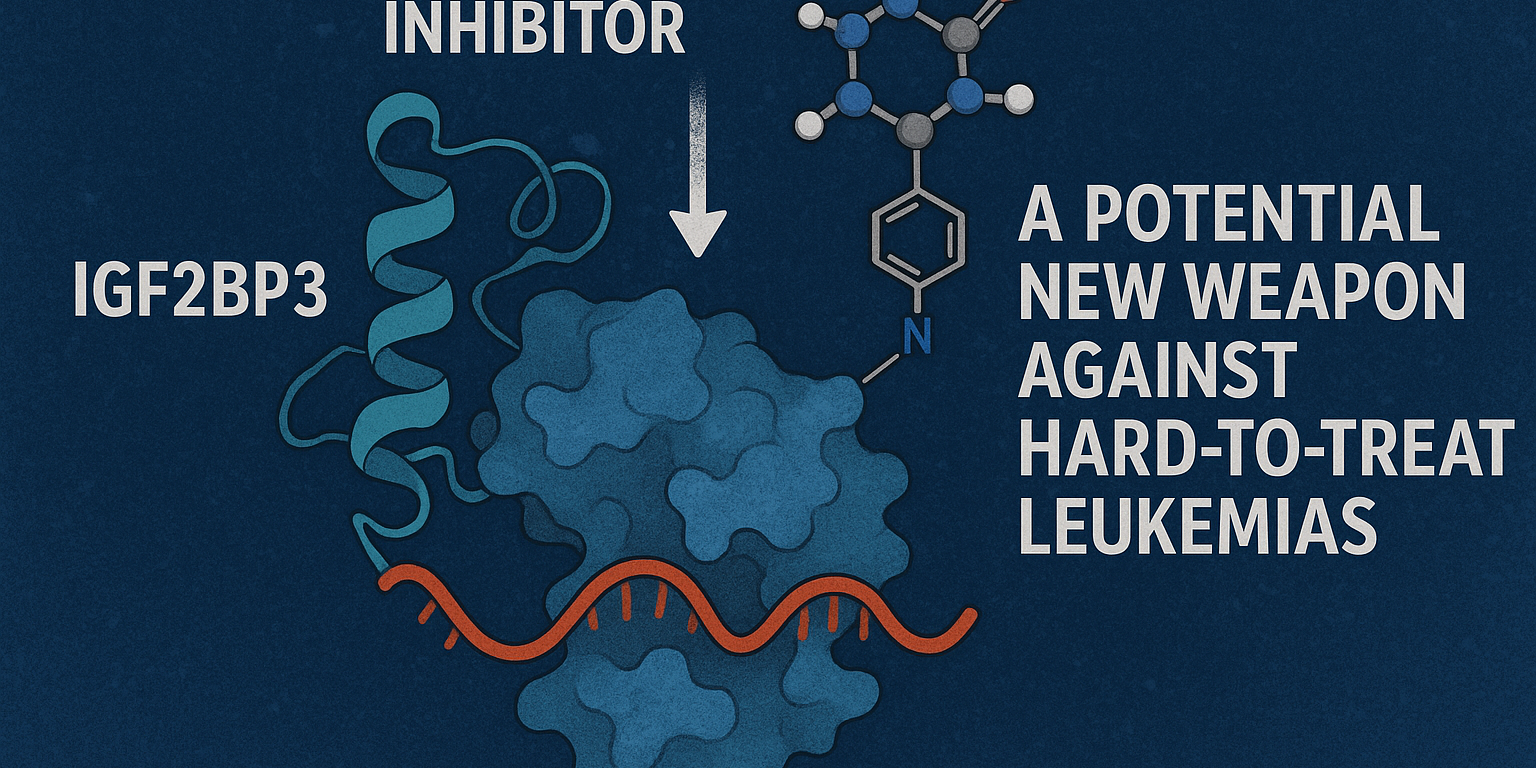
IGF2BP3 Inhibitor I3IN-002 Shows Promise Against Hard-to-Treat Leukaemia
Researchers have identified a small-molecule inhibitor of the RNA-binding protein IGF2BP3 that demonstrates potent anti-leukaemic activity in both cellular and animal models. The compound, I3IN-002, disrupts IGF2BP3–RNA interactions, suppresses leukaemia cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis — representing a major advance in targeting RNA-binding proteins long considered “undruggable.”
This discovery opens a new therapeutic avenue for aggressive leukaemias and other IGF2BP3-positive cancers with limited treatment options.
What Is IGF2BP3 and Why Does It Matter in Leukaemia?
IGF2BP3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein 3) is an oncofetal RNA-binding protein. It is highly expressed during embryonic development but is largely absent from healthy adult tissues.
In several cancers — including high-risk and therapy-resistant leukaemias — IGF2BP3 becomes aberrantly reactivated. Once expressed, it binds and stabilises oncogenic RNAs, promoting tumour cell survival, proliferation, and disease progression.
Because IGF2BP3 lacks well-defined enzymatic active sites, traditional drug discovery approaches have failed, leaving cancers driven by RNA-binding proteins without targeted therapies.
Discovery of a Small-Molecule IGF2BP3 Inhibitor

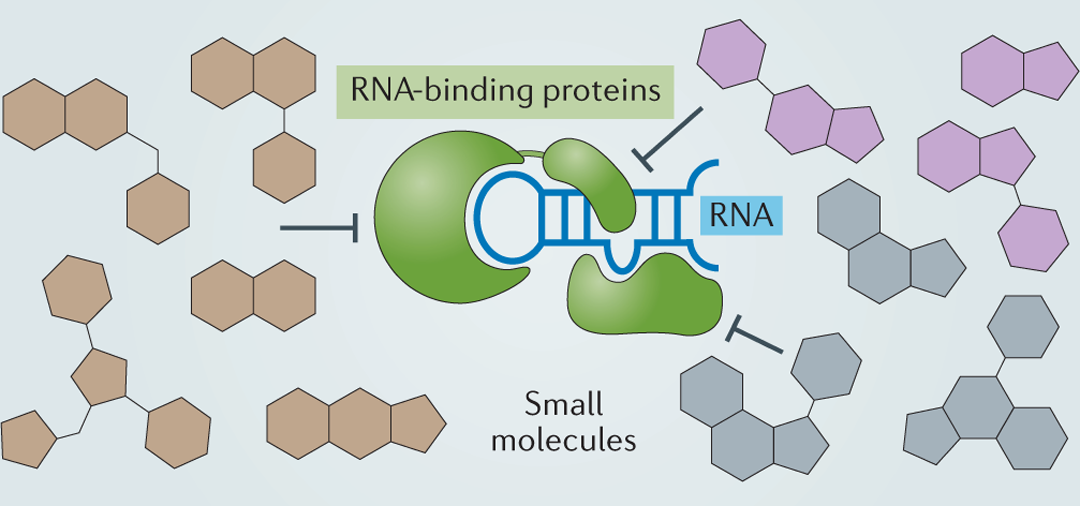
Using a high-throughput biochemical screening strategy, researchers evaluated approximately 200,000 small molecules to identify compounds capable of disrupting IGF2BP3–RNA interactions.
Following extensive counter-screening and cellular validation, a lead compound — I3IN-002 — emerged as a potent and selective IGF2BP3 inhibitor. Importantly, the compound suppressed growth only in leukaemia cell lines dependent on IGF2BP3, suggesting a mechanism-driven effect rather than general cytotoxicity.
How I3IN-002 Disrupts RNA Binding
Mechanistic studies revealed that I3IN-002 interferes directly with the RNA-binding function of IGF2BP3, destabilising its interaction with oncogenic transcripts.
In IGF2BP3-dependent leukaemia cells, treatment with I3IN-002 resulted in:
-
Altered cell-cycle progression
-
Reduced proliferative capacity
-
Increased apoptotic cell death
These effects strongly indicate that IGF2BP3’s RNA-stabilising activity is essential for leukaemia cell survival, and that pharmacological inhibition can effectively disable this oncogenic pathway.
Anti-Leukaemic Activity in Mouse Models
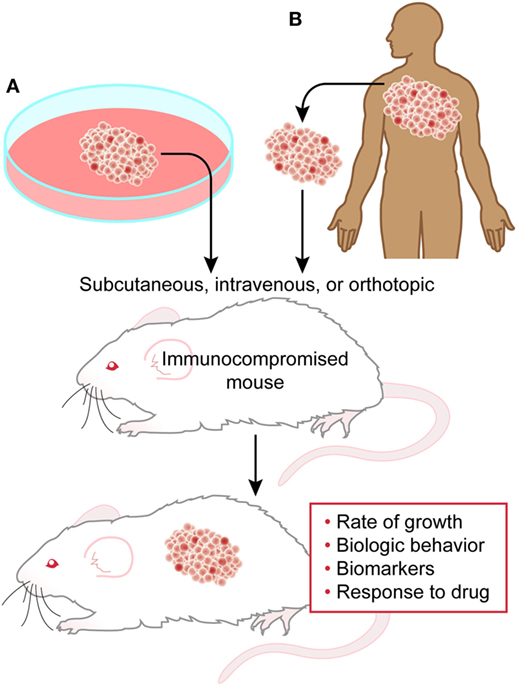

The therapeutic potential of I3IN-002 was further supported by in vivo experiments. In a transplantation mouse model of MLL-AF4-driven leukaemia, intraperitoneal administration of the compound was well tolerated and produced significant anti-leukaemic effects.
Biophysical validation assays — including cellular thermal shift assays (CETSA) and drug-affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) assays — confirmed that I3IN-002 binds IGF2BP3 in cells and disrupts RNA binding on target.
Why Targeting RNA-Binding Proteins Is a Breakthrough
The discovery of I3IN-002 has implications beyond IGF2BP3 alone.
Expanding the Druggable Cancer Target Space
RNA-binding proteins regulate post-transcriptional gene expression but have historically been excluded from drug development. This work demonstrates that RNA-binding oncoproteins can be pharmacologically inhibited using small molecules.
Precision Targeting With Reduced Toxicity
Because IGF2BP3 is largely absent from normal adult tissues, inhibitors may offer tumour-selective activity with reduced off-target toxicity compared with conventional chemotherapies.
New Options for Hard-to-Treat Cancers
For patients with poor-prognosis leukaemias or cancers lacking actionable kinase mutations, IGF2BP3 inhibitors represent a first-in-class therapeutic strategy.
Challenges and Next Steps for IGF2BP3 Inhibitors
Despite promising preclinical results, several challenges remain before clinical translation:
-
Safety and Pharmacokinetics: Comprehensive toxicology and bioavailability studies are required.
-
Selectivity Profiling: Broader interaction studies will be necessary to rule out unintended RNA-binding protein interactions.
-
Clinical Applicability: Identifying which cancer subtypes are truly IGF2BP3-dependent will be critical.
-
Resistance and Drug Delivery: As with any targeted therapy, resistance mechanisms and efficient delivery to disease sites must be addressed.
Conclusion
The identification of I3IN-002 as a small-molecule inhibitor of IGF2BP3 represents a significant step forward in cancer drug discovery. By demonstrating that an RNA-binding protein once considered “undruggable” can be effectively targeted, this research opens a new frontier in precision oncology.
If successfully translated to the clinic, IGF2BP3 inhibitors could offer new hope for patients with leukaemias and other cancers driven by RNA-binding oncoproteins.
Reference
Jaiswal AK, Scherer GM, Thaxton ML, et al.
A small molecule inhibitor of RNA-binding protein IGF2BP3 shows anti-leukemic activity.
Haematologica, Early View, 2025.
DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2025.288221